High Quality Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipes & Tubes
Seamless • Welded • Durable & Precise
Get a QuoteWhat is 316 & 316L Stainless Steel?
316 stainless steel is a molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steel that provides superior corrosion resistance compared to 304 grades. Its enhanced properties make it suitable for more aggressive environments. 316L is a low-carbon variation of the standard 316 stainless steel. Its unique properties make it ideal for various industrial applications where superior corrosion resistance and weldability are critical, particularly in chloride environments.
316 Stainless Steel
Chromium (Cr)
Nickel (Ni)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Carbon (C) Max
Manganese (Mn) Max
Silicon (Si) Max
Phosphorus (P) Max
Sulfur (S) Max
Iron (Fe)
316L Stainless Steel
Chromium (Cr)
Nickel (Ni)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Carbon (C) Max
Manganese (Mn) Max
Silicon (Si) Max
Phosphorus (P) Max
Sulfur (S) Max
Iron (Fe)
Types of Stainless Steel 316 & 316L Pipes & Tubes
As premier manufacturers in the industry, we specialize in producing both stainless steel 316/316L seamless pipes & tubes and stainless steel 316/316L welded pipes & tubes, offering comprehensive solutions for demanding industrial requirements in corrosive environments.
Manufactured from solid billets through an extrusion process, these pipes deliver superior strength and exceptional pressure resistance. Seamless construction eliminates weld seams, making them the preferred choice for critical applications involving high-pressure systems, aggressive corrosive environments, and chloride-exposed conditions where welding integrity is paramount. Their molybdenum content provides enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
These pipes provide an economical alternative with availability across a broader spectrum of sizes and dimensions. Welded pipes excel in structural applications, chemical processing systems, marine environments, and general corrosive service conditions where reliable welded joints are essential. Their cost-effectiveness combined with molybdenum-enhanced corrosion resistance makes them ideal for projects requiring superior performance in chloride-containing environments without compromising budget constraints.
Specification of Stainless Steel 316/316L Seamless & Welded Pipes And Tubes
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Pipe Specification | ASTM A312, A358 / ASME SA312, SA358 |
| SS Tube Specification | ASTM A213, A269, A249, A511, A554 / ASME SA213, SA269, SA249, SA511, SA554 |
| Pipe Size | 1/8” NB to 24” NB, 1/4” OD to 24” OD sizes |
| Tube Size | 1/2″ OD to 8″ OD |
| Thickness Range | 0.3mm – 50 mm, SCH 5, SCH10, SCH 40, SCH 80, SCH 80S, SCH 160, SCH XXS, SCH XS |
| Type | Seamless / ERW / Welded / Fabricated Pipes |
| Form | Round, Square, Rectangular, Oval, Hydraulic Etc |
| Length | Single Random, Double Random & Required Length |
| End | Plain End, Beveled End, Threaded |
| End Protection | Plastic Caps |
| Outside Finish | 2B, No.4, No.1, No.8 Mirror Finish for Stainless Steel Pipes, Finish as per customer Requirements |
| Delivery Condition | Annealed and Pickled, Polished, Bright Annealed, Cold Drawn |
| Inspection, Test Reports | Mill Test Certificates, EN 10204 3.1, Chemical Reports, Mechanical Reports, PMI Test Reports, Visual Inspection Reports, Third Party Inspection Reports, NABL Approved Lab Reports, Destructive Test Report, Non Destructive Test Reports |
| Packing | Packed in Wooden Boxes, Plastic Bags, Steel Strips Bundled, or as per Customers Requests |
| Specials | Sizes and Specifications other than above can be manufactured on request |
STAINLESS STEEL PIPE & TUBES SCHEDULE DIMENSIONS WALL THICKNESS, WT./MTR. (KG)
Click to expand ▼
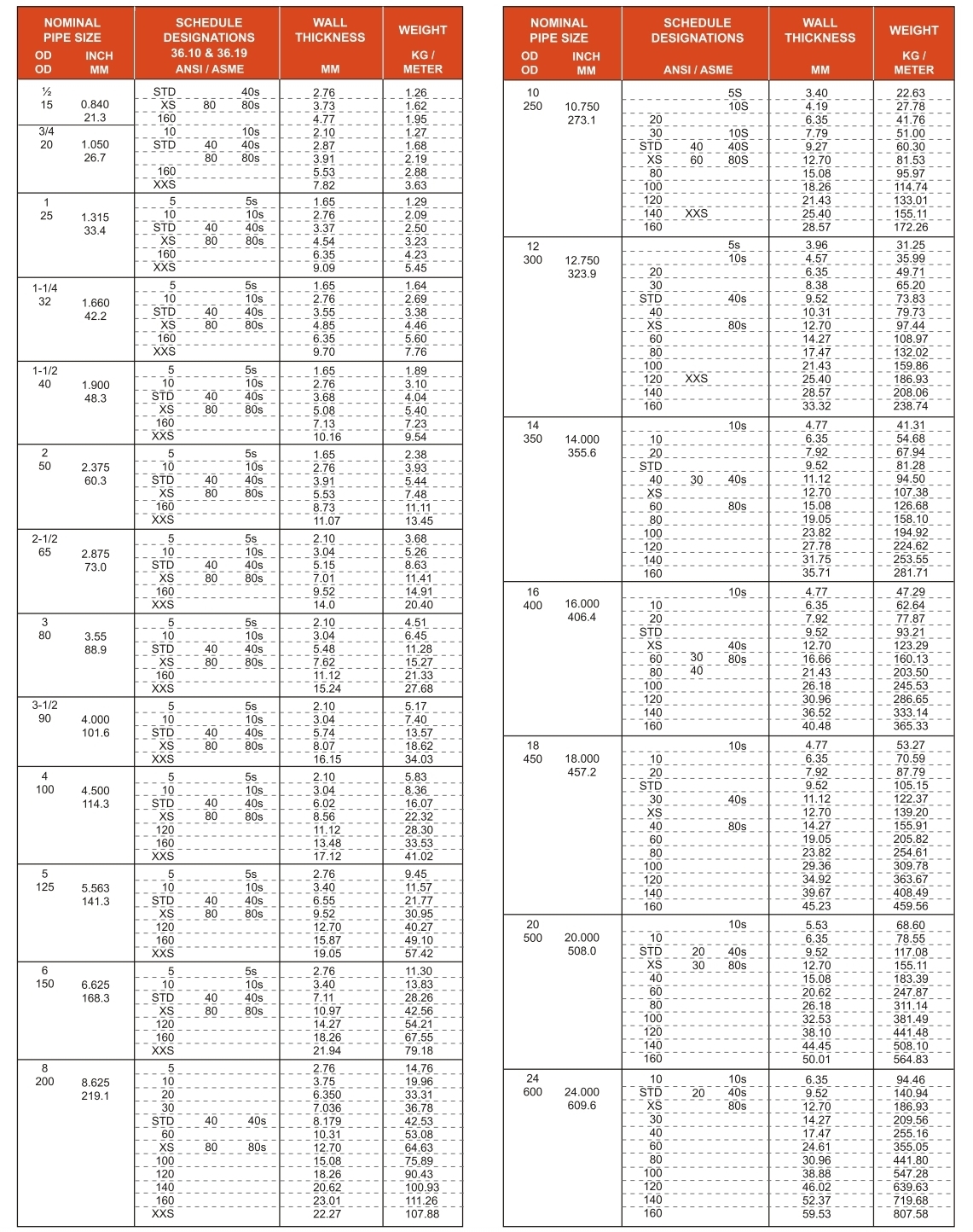
Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipe Dimensions & Weight Chart
| OD (mm) | WT (mm) | NPS (dn) | Schedule | Weight (kg/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.72 | 1.65 | 1/4″ | 10S | 0.50 |
| 13.72 | 2.24 | 1/4″ | 40S | 0.64 |
| 13.72 | 3.02 | 1/4″ | 80S | 0.81 |
| 17.15 | 1.65 | 3/8″ | 10S | 0.64 |
| 17.15 | 2.31 | 3/8″ | 40S | 0.86 |
| 17.15 | 3.20 | 3/8″ | 80S | 1.12 |
| 21.34 | 2.11 | 1/2″ | 10S | 1.02 |
| 21.34 | 2.77 | 1/2″ | 40S | 1.29 |
| 21.34 | 3.73 | 1/2″ | 80S | 1.65 |
| 26.67 | 2.11 | 3/4″ | 10S | 1.30 |
| 26.67 | 2.87 | 3/4″ | 40S | 1.71 |
| 26.67 | 3.91 | 3/4″ | 80S | 2.23 |
| 33.40 | 2.77 | 1″ | 10S | 2.13 |
| 33.40 | 3.38 | 1″ | 40S | 2.54 |
| 33.40 | 4.55 | 1″ | 80S | 3.29 |
| 48.26 | 2.77 | 1.1/2″ | 10S | 3.16 |
| 48.26 | 3.68 | 1.1/2″ | 40S | 4.11 |
| 48.26 | 5.08 | 1.1/2″ | 80S | 5.49 |
| 60.33 | 2.77 | 2″ | 10S | 3.99 |
| 60.33 | 3.91 | 2″ | 40S | 5.52 |
| 60.33 | 5.54 | 2″ | 80S | 7.60 |
| 88.90 | 3.05 | 3″ | 10S | 6.56 |
| 88.90 | 5.49 | 3″ | 40S | 11.47 |
| 88.90 | 7.62 | 3″ | 80S | 15.51 |
Stainless Steel 316/316L Tube Size Chart
| Wall Thickness (in) | Available Sizes (in) |
|---|---|
| 0.028″ | 1/16″; 1/8″; 3/16″; 1/4″; 5/16″; 3/8″ |
| 0.035″ | 1/8″; 3/16″; 1/4″; 5/16″; 3/8″; 1/2″; 5/8″; 3/4″; 1″; 1-1/4″; 1-1/2″; 2″ |
| 0.049″ | 1/8″; 3/16″; 1/4″; 5/16″; 3/8″; 1/2″; 5/8″; 3/4″; 1″; 1-1/4″; 1-1/2″; 2″ |
| 0.065″ | 3/16″; 1/4″; 5/16″; 3/8″; 1/2″; 5/8″; 3/4″; 1″; 1-1/4″; 1-1/2″; 2″ |
| 0.083″ | 1/4″; 5/16″; 3/8″; 1/2″; 5/8″; 3/4″; 1″; 1-1/4″; 1-1/2″; 2″; 2-1/2″; 3″ |
| 0.095″ | 1/4″; 3/8″; 1/2″; 5/8″; 3/4″; 1″; 1-1/4″; 1-1/2″; 2″; 2-1/2″; 3″ |
| 0.120″ | 1/2″; 5/8″; 3/4″; 1″; 1-1/4″; 1-1/2″; 2″; 2-1/2″; 3″ |
Pressure Ratings for SS 316/316L Tubing (PSIG)
| OD (in) | WT 0.028″ | WT 0.035″ | WT 0.049″ | WT 0.065″ | WT 0.083″ | WT 0.095″ | WT 0.109″ | WT 0.120″ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 7,900 | 10,100 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 1/4″ | 3,700 | 5,800 | 7,900 | 9,500 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 5/16″ | N/A | 3,700 | 5,400 | 7,300 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 3/8″ | N/A | 3,100 | 4,400 | 6,100 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 1/2″ | N/A | 2,300 | 3,200 | 4,400 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 3/4″ | N/A | N/A | 2,100 | 2,900 | 3,900 | 4,500 | N/A | N/A |
| 1″ | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2,200 | 2,900 | 3,400 | 3,900 | 4,300 |
Chemical Composition of Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipes and Tubes
| Element | 316 Stainless Steel (%) | 316L Stainless Steel (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.08 max | 0.030 max |
| Manganese (Mn) | 2.00 max | 2.00 max |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.045 max | 0.045 max |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.030 max | 0.030 max |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.75 max | 0.75 max |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.00 – 18.00 | 16.00 – 18.00 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10.00 – 14.00 | 10.00 – 14.00 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.00 – 3.00 | 2.00 – 3.00 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.10 max | 0.10 max |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance | Balance |
Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipes and Tubes
| Grade | Tensile Strength (MPa) min | Yield Strength (MPa) min | Elongation (% in 2″) min | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | Rockwell B (95) max Brinell (217) max |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | Rockwell B (95) max Brinell (217) max |
Physical Properties of Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipes and Tubes
| Grade | Density (kg/m³) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (μm/m°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m.K) | Specific Heat 0-100°C (J/kg.K) | Electrical Resistivity (nΩ.m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316/316L | 8000 | 193 | 15.9 (0-100°C) 16.2 (0-315°C) 17.5 (0-538°C) |
16.3 (at 100°C) 21.5 (at 500°C) |
500 | 740 |
Equivalent Grades for Stainless Steel 316/316L Pipes and Tubes
| STANDARD | WERKSTOFF NR. | UNS | JIS | AFNOR | BS | GOST | EN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS316 | 1.4401 / 1.4436 | S31600 | SUS316 | Z6CND17-11-02 | 316S31 | 08X17H13M2 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 |
| SS316L | 1.4404 / 1.4435 | S31603 | SUS316L | Z3CND17-11-02 | 316S11 | 03X17H13M2 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 |
💡 Practical Difference in Use
Use 316 when: higher strength and hardness are required for structural applications with minimal welding.
→ Example: structural components in marine environments, high-temperature applications, mechanical parts requiring extra strength.
Use 316L when: extensive welding is involved or in highly corrosive environments, particularly those containing chlorides. → Example: chemical processing equipment, marine applications, pharmaceutical systems, and equipment exposed to saltwater or strong acids.
Uses of 316/316L Stainless Steel Pipes
The uses are defined by its superior corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and acids, along with excellent high-temperature performance. These pipes are essential for conveying aggressive substances in demanding environments.
- Transporting Highly Corrosive Liquids & Gases: This is its primary advantage over 304 grades. It’s used for moving aggressive chemicals, saltwater, chlorinated compounds, and various process streams in harsh environments.
- Marine and Coastal Applications: 316/316L pipes are extensively used in marine environments for seawater handling, offshore platforms, shipbuilding, and coastal infrastructure where salt corrosion is a major concern.
- High-Purity and Critical Systems: With proper polishing and connections, 316L pipes form the backbone of ultra-pure systems in pharmaceutical, biotech, and semiconductor industries where maximum corrosion resistance and cleanability are essential.
When to Choose 316L vs. Higher Alloys?
This is a critical consideration. 316L is the premium standard for chloride resistance among standard austenitic grades. It contains Molybdenum (2-3%), which gives it significantly better resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion compared to 304 grades.
Choose 316L when:
- The environment contains moderate to high chlorides (saltwater, coastal air, road salts, bleach solutions).
- Processing acidic chemicals like sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, or organic acids at moderate concentrations.
- Applications require superior pitting resistance with cost-effectiveness compared to super austenitic grades.
Upgrade to Higher Alloys when:
- Extremely high chloride concentrations or temperatures exceed 316L’s capabilities.
- Applications involve highly oxidizing acids like hot concentrated sulfuric acid.
- Environments with risk of stress corrosion cracking in stagnant chloride solutions.
Industries That Use 316/316L Stainless Steel Pipes
316/316L stainless steel pipes are essential in industries requiring superior corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and aggressive chemicals. Here are the primary industries that rely on these grades:
This industry extensively uses 316/316L for handling aggressive chemicals and acids where standard 304 grades would fail.
Uses
Process piping for sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, chlorinated compounds, dye stuffs, and chemical intermediates. Heat exchangers, reactor systems, and distillation columns.
Why 316/316L?
Superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, particularly acidic environments. Molybdenum content provides excellent pitting and crevice corrosion resistance.
This industry demands the highest standards of purity and corrosion resistance for critical processes.
Uses
High-purity water systems, WFI (Water for Injection) distribution, process piping for active pharmaceutical ingredients, clean steam systems, and bioreactors.
Why 316L?
Excellent corrosion resistance against cleaning agents and sterilants. Prevents metallic contamination and maintains system integrity through repeated sterilization cycles.
Essential for applications exposed to seawater, salt spray, and marine atmospheres.
Uses
Seawater cooling systems, ballast water piping, firefighting systems, hydraulic lines on ships and offshore platforms, desalination plant components.
Why 316/316L?
Superior resistance to chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion. Maintains structural integrity in saltwater environments where 304 would rapidly corrode.
Critical for handling aggressive bleaching chemicals and process streams in paper manufacturing.
Uses
Bleach plant piping, chemical recovery systems, black liquor lines, and digestor systems handling chloride-containing process streams.
Why 316/316L?
Resists corrosion from chlorine compounds, chlorides, and acidic by-products generated during the pulping and bleaching processes.
Widely used in both upstream and downstream applications, particularly where chlorides are present.
Uses
Production tubing, wellhead components, injection systems, process piping in refineries, and offshore platform utilities exposed to seawater.
Why 316/316L?
Resists sour service conditions, chloride stress corrosion cracking, and provides reliable performance in both sweet and mildly sour environments.
Used in applications requiring enhanced corrosion resistance beyond 304 capabilities.
Uses
High-salt content food processing, pickle and brine lines, vinegar production, and systems using aggressive cleaning chemicals.
Why 316L?
Superior resistance to chlorides in cleaning solutions and salt-containing food products. Maintains hygiene standards in aggressive processing environments.
Preferred for structures in aggressive environments where appearance and longevity are critical.
Uses
Handrails, facades, and structural elements in coastal areas, swimming pool structures, and architectural features in polluted urban environments.
Why 316/316L?
Excellent resistance to atmospheric corrosion from salt spray and industrial pollutants. Maintains aesthetic appearance in harsh environmental conditions.
Critical for various systems in conventional and nuclear power plants.
Uses
Condenser tubes, feedwater systems, cooling water piping, flue gas desulfurization systems, and nuclear auxiliary systems.
Why 316/316L?
Resists corrosion from chlorides in cooling water and provides reliable performance in high-temperature aqueous environments encountered in power generation.
Request a Quote
Looking for premium 316 | 316L Pipes & Tubes? Contact us today to get the best prices.
Contact Us